Greenhouse structures play a crucial role in sustainable agriculture and gardening. These structures provide controlled environments for plants, allowing them to thrive in optimal conditions regardless of external elements.
The greenhouse structure, however, regulates temperature, humidity, and ventilation, creating an ideal environment for plant growth.
They promote effective resource use and keep the impact of climate change on crop growth.
Here are different types of greenhouse structures under Different categories:
1. Traditional Greenhouse Structures
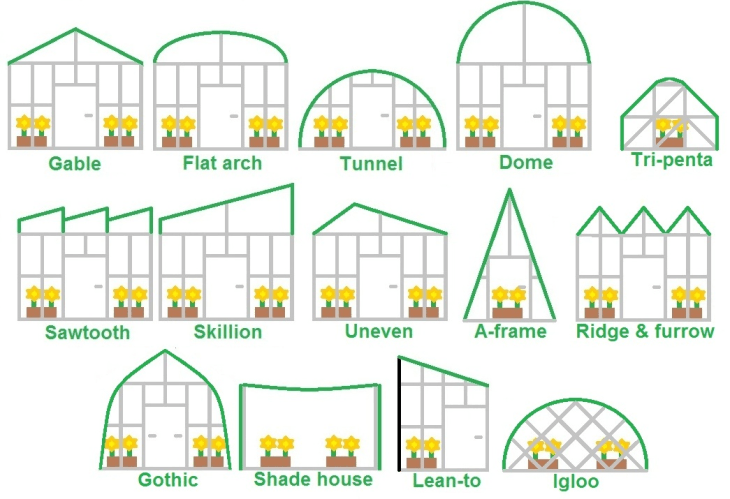
A. Venlo Greenhouse
The Venlo greenhouse is a type of traditional greenhouse structure known for its rectangular shape and distinctive roof design. It features a series of pitched roofs with multiple ridges and gutters running along its length.
The structure is typically made of aluminum or steel frames with glass or polycarbonate panels.
Characteristics of Venlo Greenhouse:
Rectangular Shape: Venlo greenhouses have a rectangular layout, which optimizes space utilization and facilitates efficient plant arrangement.
Gutter-Connected: These greenhouses are often gutter-connected, meaning they can be linked together in a row to create larger growing areas.
Roof Design: The Venlo greenhouse’s roof design allows for excellent natural ventilation and light distribution, thanks to its ridge and furrow arrangement.
Advantages of Venlo Greenhouse:
Optimal Light Transmission: The glass or polycarbonate panels provide high light transmission, promoting plant growth and productivity.
Excellent Ventilation: The roof design allows for efficient natural ventilation, helping regulate temperature and humidity.
Space Efficiency: The rectangular layout maximizes growing space, making it suitable for commercial cultivation.
Disadvantages of Venlo Greenhouse:
Costly Construction: Building a Venlo greenhouse can be relatively expensive due to the materials used. The cost range for a Venlo greenhouse typically varies between $10 and $30 per square foot, depending on size, materials, and specific customization options.
Vulnerable to Hail: Glass panels are susceptible to damage from hailstorms, requiring protective measures.
B. Gothic Arch Greenhouse
The Gothic arch greenhouse, also known as a hoop house or tunnel greenhouse, is a simpler and more cost-effective traditional greenhouse structure.
Its rounded or arched shape characterizes it, and it is typically made of steel or PVC pipes covered with polyethylene or other plastic films.
Characteristics of Gothic Arch Greenhouse:
Arched Design: Gothic arch greenhouses have a curved, semi-circular, or pointed arch roof shape.
Lightweight Structure: These greenhouses are lightweight and easy to assemble, making them suitable for small-scale and temporary use.
Affordable Materials: The use of plastic films and simpler frame materials reduces construction costs.
Advantages of Gothic Arch Greenhouse:
Cost-Effective: Gothic arch greenhouses are budget-friendly and ideal for hobbyists or small-scale growers. The cost range for a Gothic Arch greenhouse typically falls between $5,000 and $20,000, depending on size, materials, and additional features.
Quick Assembly: They can be assembled relatively quickly, allowing for faster cultivation.
Season Extension: These greenhouses can extend the growing season and protect plants from adverse weather conditions.
Disadvantages of Gothic Arch Greenhouse:
Limited Durability: The materials used are less durable than glass or polycarbonate and may require more frequent replacement.
Gothic Arch greenhouses are durable and can last for 20 to 30 years or longer with proper care.
Limited Space: Due to their arched design, they may have limited headroom, which can restrict plant growth and access.
In summary, traditional greenhouse structures like the Venlo greenhouse offer advanced features, while the Gothic arch greenhouse provides a more affordable and accessible option for growers.
The decision depends on budget, space needs, and how long it lasts.
2. Modern Greenhouse Structures
A. Hoop House Greenhouse
Hoop house greenhouses, also known as tunnel or high tunnel greenhouses, are modern greenhouse structures characterized by their simple yet effective design.
These structures are typically made of curved steel or PVC pipes covered with a single or double layer of polyethylene plastic.
Key Features and Benefits of Hoop House Greenhouse:
Affordable Construction: Hoop houses are cost-effective to build compared to traditional greenhouses, making them accessible to small-scale growers.
Quick Assembly: They can be assembled relatively quickly, allowing for rapid deployment and season extension.
Natural Ventilation: Hoop houses often have roll-up sides or end vents, which promote natural ventilation and temperature control.
Increased Crop Yield: These structures help protect crops from adverse weather conditions, pests, and diseases, resulting in improved yields.
Versatility: Hoop houses are versatile and can be used for various crops, including vegetables, fruits, and flowers.
B. Quonset Greenhouse
Quonset greenhouses are a type of modern greenhouse characterized by their semi-circular or Quonset hut-like shape. They are typically constructed using curved metal or plastic frames and covered with polyethylene or polycarbonate panels.
Advantages of Quonset Greenhouse:
Sturdy Design: The curved shape of Quonset greenhouses provides structural strength and durability.
Excellent Light Transmission: They offer high light transmission, promoting optimal plant growth.
Wide Range of Sizes: Quonset greenhouses come in various sizes, suitable for both small-scale and commercial operations.
Temperature Control: With proper ventilation and heating systems, Quonset greenhouses allow growers to control temperature and humidity effectively.
Longevity: When maintained properly, Quonset greenhouses can have a long lifespan, making them a good investment.
Disadvantages of Quonset Greenhouse:
Limited Headroom: The curved shape of Quonset greenhouses can restrict vertical space, limiting the types of crops that can be grown and making it challenging to work inside.
Condensation Issues: The curved roof design can lead to condensation buildup, which may negatively affect plant health and require additional ventilation or dehumidification measures.
Less Efficient Insulation: The curved walls of Quonset greenhouses may provide less insulation compared to other greenhouse designs, potentially leading to temperature fluctuations and increased heating costs.
Limited Customization: Quonset greenhouses have a fixed shape, limiting the flexibility to customize the layout and space utilization for specific growing needs.
Vulnerable to Snow Load: In areas with heavy snowfall, the curved roof design may not be as effective at shedding snow, leading to potential structural issues or the need for additional support.
Reduced Aesthetic Appeal: Some growers may find the appearance of Quonset greenhouses less aesthetically pleasing compared to other greenhouse designs, which may matter in certain settings or for retail purposes.
C. High Tunnel Greenhouse
High tunnel greenhouses are a variation of hoop houses characterized by their taller and narrower design. They are often used for season extension and protection of crops from adverse weather conditions.
Features, Benefits, and Applications of High Tunnel Greenhouses:
Season Extension: High tunnel greenhouses allow growers to extend the growing season, enabling earlier planting and later harvests.
Improved Crop Quality: They protect from frost, wind, and heavy rain, resulting in better crop quality.
Low Cost: High tunnel greenhouses are cost-effective to build and maintain, making them suitable for small farms and market gardeners.
Adaptability: These structures can be used for various crops, including vegetables, berries, and flowers.
Natural Ventilation: Many high tunnel designs incorporate roll-up sidewalls for natural ventilation.
In conclusion, modern greenhouse structures like hoop houses, Quonset greenhouses, and high tunnel greenhouses offer cost-effective and efficient solutions for extending the growing season and protecting crops.
Their features and benefits make them suitable for a wide range of growers, from small-scale farmers to commercial operations.
3. Specialized Greenhouse Structures
A. Reading Greenhouse
Introduction and Use in Research and Education:
A reading greenhouse is a specialized type primarily designed for research and education. Unlike traditional greenhouses used for commercial cultivation, reading greenhouses are focused on creating controlled environments for scientific experimentation and learning.
Key Features of Reading Greenhouse:
Precise Climate Control: Reading greenhouses are equipped with advanced climate control systems, including temperature, humidity, and light regulation, allowing researchers to create specific environmental conditions for experiments.
Modular Design: These greenhouses often have a modular layout, enabling researchers to customize the space for different research projects and educational activities.
Data Monitoring: They have sensors and data logging systems to monitor and record environmental parameters, facilitating research data collection and analysis.
Access to Natural Light: Reading greenhouses incorporate natural light, mimicking outdoor conditions when needed, while also providing the option for a complete blackout for controlled experiments.
Teaching Facilities: In educational settings, reading greenhouses may have classrooms or observation areas, making them ideal for teaching students about plant biology and environmental science.
B. Aquaponic Greenhouse
Combining Fish Farming and Plant Cultivation:
Aquaponic greenhouses are specialized structures that integrate aquaculture (fish farming) with hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation).
This innovative system creates a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants, where fish waste provides nutrients for plant growth, and the plants filter and purify the water for the fish.
Key Features and Benefits of Aquaponic Greenhouses:
Sustainable Farming: Aquaponics is an eco-friendly approach that minimizes water usage and nutrient waste while producing both fish and vegetables in a closed-loop system.
High Yields: This system allows for year-round cultivation of crops and can produce higher yields compared to traditional farming methods.
Nutrient-rich produce: Plants in aquaponic systems receive a balanced nutrient supply from fish waste, resulting in healthy and nutritious produce.
Reduced Environmental Impact: It reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and can be operated with minimal use of pesticides.
Education and Research: Aquaponic greenhouses serve as educational tools for teaching sustainable agriculture and provide opportunities for research in the field of aquaponics.
C. Vertical Greenhouse
Maximizing Space with Vertical Farming Techniques:
Vertical greenhouses are specialized structures designed to maximize space efficiency by growing plants vertically. These greenhouses utilize advanced technology and vertical farming techniques to cultivate crops in stacked layers or towers.
Key Features and Benefits of Vertical Greenhouses:
Space Efficiency: Vertical farming allows for the cultivation of a large number of plants in a relatively small footprint, making it suitable for urban agriculture.
Year-Round Production: Controlled environments in vertical greenhouses enable year-round crop production regardless of external weather conditions.
Resource Efficiency: Vertical farming optimizes resource use, including water, nutrients, and energy, resulting in reduced environmental impact.
Precision Control: These structures employ automated systems to monitor and adjust environmental conditions, ensuring optimal plant growth.
Innovative Crop Variety: Vertical greenhouses provide a platform for experimenting with different crop varieties and specialty crops.
In summary, specialized greenhouse structures such as reading, aquaponic, and vertical greenhouses serve specific purposes, ranging from research and education to sustainable agriculture and efficient space utilization.
4. Sustainable and Innovative Greenhouse Structures

A. Passive Solar Greenhouse
Harnessing Solar Energy for Heating:
A passive solar greenhouse is a sustainable and energy-efficient structure designed to capture and utilize solar energy for heating, reducing the need for conventional heating systems.
Key Features and Benefits:
Solar Orientation: Passive solar greenhouses are strategically oriented to maximize exposure to the sun, capturing sunlight for natural heating.
Thermal Mass: They incorporate thermal mass materials like concrete or water barrels to store and release heat gradually, maintaining stable temperatures.
Heat Distribution: Proper ventilation and air circulation systems distribute the collected heat throughout the greenhouse, keeping plants warm.
Energy Savings: By relying on solar heat, these greenhouses significantly reduce energy consumption, making them environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
Extended Growing Seasons enable year-round cultivation by providing consistent warmth during colder months.
B. Geodesic Dome Greenhouse
Aesthetics, Durability, and Energy Efficiency:
A geodesic dome greenhouse is a unique and visually appealing structure known for its spherical or hemispherical shape. It offers several advantages, including durability and energy efficiency.
Key Features and Benefits:
Aesthetic Appeal: Geodesic domes have a striking appearance that enhances the visual appeal of the greenhouse, making it a unique addition to any environment.
Structural Strength: The rounded shape is naturally sturdy and can endure strong winds and heavy snow, ensuring it lasts long.
Energy Efficiency: Their efficient shape minimizes heat loss, making it easier to maintain a stable and energy-efficient environment for plant growth.
Space Optimization: Geodesic domes provide ample growing space while requiring fewer construction materials compared to traditional rectangular structures.
Natural Ventilation: Ventilation systems can be integrated into the dome’s design to ensure proper airflow and temperature regulation.
C. Greenhouse Integrated with Renewable Energy Systems
Harnessing Wind or Solar Power:
Greenhouses integrated with renewable energy systems utilize wind turbines or solar panels to generate electricity for various greenhouse functions, including heating, lighting, and ventilation.
Key Features and Benefits:
Energy Independence: These greenhouses reduce reliance on conventional energy sources, making them more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Cost Savings: By generating their electricity, these greenhouses can save on energy costs in the long run.
Reduced Carbon Footprint: Using renewable energy cuts down on the greenhouse gasses linked to traditional energy.
Energy Storage: Some systems include energy storage solutions like batteries to ensure a consistent power supply even when renewable sources are not available.
Adaptability: These systems can be customized to suit the greenhouse’s specific energy needs and local conditions.
In conclusion, sustainable and innovative greenhouse structures like passive solar greenhouses, geodesic dome greenhouses, and those integrated with renewable energy systems represent a forward-thinking approach to agriculture.
They prioritize energy efficiency, durability, and environmental responsibility while providing suitable environments for plant growth. These technologies play a crucial role in addressing the challenges of modern agriculture while minimizing its environmental impact.
Some relevant Questions on the Types of Greenhouse Structures
1. What are the different types of greenhouse structures?
Greenhouse structures can be categorized into several types, including hoop houses, Quonset houses, gutter-connected houses, and Gothic arch greenhouses, each with its own design and advantages.
2. What is a hoop house greenhouse?
A hoop house is a simple, cost-effective greenhouse structure with a curved, hoop-like frame covered with plastic or polyethylene. It is easy to assemble and suitable for season extension and plant protection.
3. What is a Quonset house greenhouse?
A quonset house is a rounded, arched structure often made of galvanized steel pipes. It offers good strength and durability, making it suitable for various climates and crops.
4. What are gutter-connected greenhouses?
Gutter-connected greenhouses consist of multiple greenhouse bays connected with a central gutter system. They provide scalability and better climate control compared to standalone structures.
5. What is a Gothic arch greenhouse?
A Gothic arch greenhouse features a curved, pointed roof that offers better snow shedding and allows for increased height and air circulation. It’s ideal for taller crops and regions with heavy snowfall.
6. Are there different materials used for greenhouse covers?
Yes, greenhouse covers can be made of materials like glass, polycarbonate, polyethylene, or shade cloth, each with specific properties affecting light transmission, insulation, and durability.
7. What is a lean-to greenhouse?
A lean-to greenhouse is connected to another building, like a house or a structure. It shares one wall with the supporting structure, utilizing its thermal mass for temperature regulation.
8. What is a cold frame greenhouse?
A cold frame is a simple, unheated greenhouse designed for season extension and protection of cold-tolerant plants during the winter or early spring. It relies on passive solar heat for warming.
9. Are there greenhouses designed for specific climates?
Yes, some greenhouses are designed for specific climates, with features and materials tailored to accommodate the unique climate and weather conditions of different regions.
10. Can I customize the size and shape of my greenhouse structure?
Yes, you can customize the size and shape of your greenhouse structure to suit your specific gardening needs and available space.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting the right greenhouse structure is crucial for meeting specific needs and goals in greenhouse gardening.
Different types of greenhouse structures come within modern, specialized, traditional, sustainable, and innovative greenhouses.
However, embracing sustainable and efficient greenhouse practices is essential for minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact.
By implementing the right greenhouse structure and practicing sustainability, gardeners can create optimal conditions for plant growth while minimizing resource usage and maximizing productivity.

