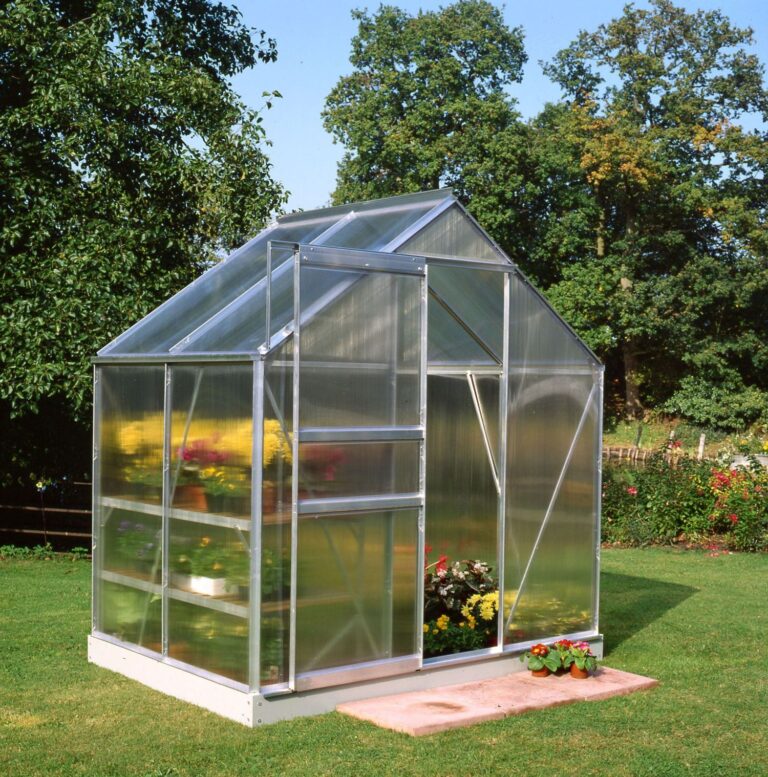
One morning in my garden, I thought about making my own greenhouse. I had a puzzling question: “Is 4mm polycarbonate good for a greenhouse?” I liked the idea of taking care of my plants, protecting them from bad weather, and letting them grow longer. But the stuff you use to build a greenhouse was confusing. I wanted to figure it out.
I started looking for answers. I checked out gardening websites, talked to people who know about gardens, and even argued with my friends about what makes the best greenhouse cover. I found a lot of information, stories, and different opinions, all saying how important the cover material is.
So, why don’t you join me as we dive into the world of greenhouse materials? Let’s do this together!
A 4mm polycarbonate panel can be used in a greenhouse, but its suitability depends on factors like climate, budget, and intended use. Thicker panels offer better insulation and durability, making them ideal for harsh climates, though they may cost more. Thinner panels allow more light but may require extra measures in extreme weather. Consider your specific needs and local conditions when choosing the panel thickness for your greenhouse.
What Are the Best Types of Greenhouse Covering Materials?
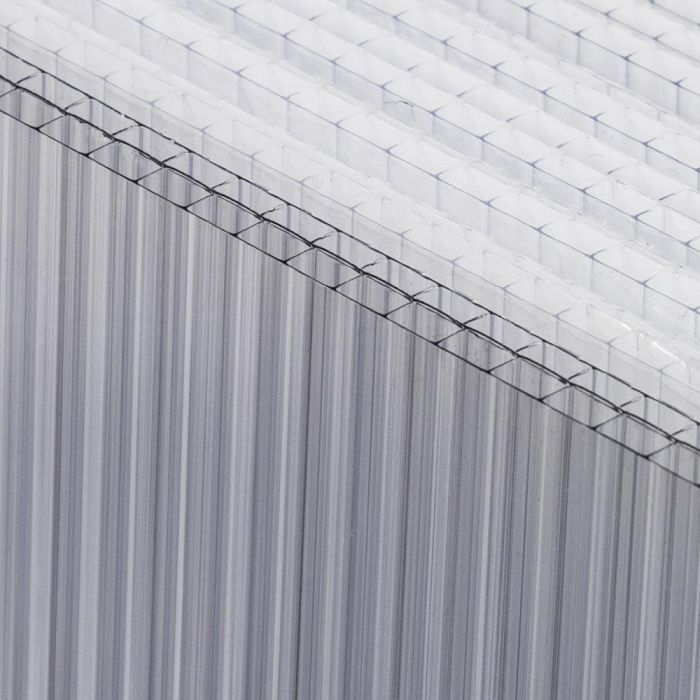

When it comes to selecting the ideal greenhouse covering material, various options are available, each with its unique advantages and considerations.
Polycarbonate:
Polycarbonate panels are a popular choice for greenhouse covering due to their versatility. They come in various thicknesses, such as 4mm, 6mm, 8mm, and 10mm, allowing growers to choose based on specific needs. Polycarbonate is known for its impact resistance, making it less likely to shatter compared to glass.
In addition, it has excellent light transmission properties, crucial for plant growth. Polycarbonate also provides insulation, which helps regulate temperature inside the greenhouse. Moreover, UV-resistant coatings are often applied to polycarbonate to protect plants from harmful radiation.
While more expensive than some alternatives, the long lifespan of polycarbonate can make it cost-effective over time.
Glass:
Glass is a traditional greenhouse material known for its clarity and aesthetics.It offers excellent light transmission, allowing for optimal plant growth and visibility. Glass is durable and can last for many years if properly maintained.
However, it is heavy and can be prone to breakage, posing safety concerns. Glass greenhouses may require additional heating in colder climates due to poor insulation properties. Installation of glass can be more expensive and labor-intensive compared to other materials.
Polyethylene:
Polyethylene plastic is a cost-effective option for greenhouse coverings. It comes in the form of plastic sheets or films, which are easy to install.
Polyethylene provides good insulation and diffuses light, reducing the risk of sunburn for plants. However, it has a shorter lifespan compared to polycarbonate and glass, and it may need replacement sooner.
In addition, it is less durable and more susceptible to tears and damage from hail or strong winds.
Polycarbonate vs. Other Materials:
| Property | Polycarbonate | Glass | Polyethylene |
| Durability | High | Low | Moderate |
| Insulation | Excellent | Poor | Poor |
| Light Transmission | Good | Excellent | Good |
| UV Resistance | Excellent | Limited | Limited |
| Impact Resistance | High | Low | Low |
| Clarity | Good | Excellent | Poor |
| Cost | Moderate | High | Low |
| Replacement Frequency | Infrequent | N/A (repairable) | Frequent |
| Maintenance | Low | Low | Low |
| Suitable Climates | Versatile, All Climates | Controlled Environments | Moderate Climates |
What Are the Top Advantages of Polycarbonate for Greenhouses?
Polycarbonate has become a popular choice for greenhouse construction, thanks to its remarkable qualities.
Durability:
Polycarbonate is highly durable and can withstand harsh weather conditions, including hail and snow. Its impact resistance minimizes the risk of breakage, making it a safer choice.
Insulation:
Polycarbonate offers good insulation, helping to maintain stable temperatures inside the greenhouse. Moreover, this insulation property can reduce heating costs and protect plants from temperature extremes.
Light Transmission:
Polycarbonate provides excellent light transmission, allowing for optimal photosynthesis and plant growth. It diffuses light evenly, reducing the risk of hot spots or shading.
UV Resistance:
UV-resistant coatings on polycarbonate panels protect plants from harmful ultraviolet radiation, preventing sunburn and damage.
Impact Resistance:
Polycarbonate’s impact resistance makes it less prone to damage from hail, wind-blown debris, or accidental impacts, ensuring a longer lifespan for the greenhouse covering.
What Factors to Consider When Choosing Polycarbonate Thickness?
When selecting the right polycarbonate thickness for your project, several critical factors come into play.
Climate and Weather Conditions:
The local climate plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate polycarbonate thickness.
In regions with harsh winters or extreme weather conditions, thicker polycarbonate panels (e.g., 8mm or 10mm) are advisable to provide better insulation and withstand snow loads and wind.
Greenhouse Design and Size:
The design and size of the greenhouse effect the choice of polycarbonate thickness. Larger greenhouses may require thicker panels to maintain structural integrity and insulation.
However, the shape of the greenhouse (e.g., arched or gabled) can also influence thickness requirements.
Budget:
Budget considerations are essential when choosing polycarbonate thickness. Thicker panels are generally more expensive than thinner ones, so it’s crucial to strike a balance between cost and performance.
In addition, consider the long-term cost savings in terms of energy efficiency and reduced maintenance when investing in thicker polycarbonate.
Desired Lifespan:
Your greenhouse’s intended lifespan should influence your choice of polycarbonate thickness. Thicker panels often have a longer lifespan due to increased durability.
However, if you plan to use the greenhouse for many years, investing in thicker polycarbonate may be worthwhile.
Energy Efficiency:
Thicker polycarbonate panels typically offer better insulation, which can enhance energy efficiency. Improved insulation can reduce heating costs in colder climates and minimize cooling expenses in hot regions.
Additionally, consider the greenhouse’s energy requirements and the potential for energy savings when selecting panel thickness.
How Does 4mm Polycarbonate Fare for a Greenhouse?
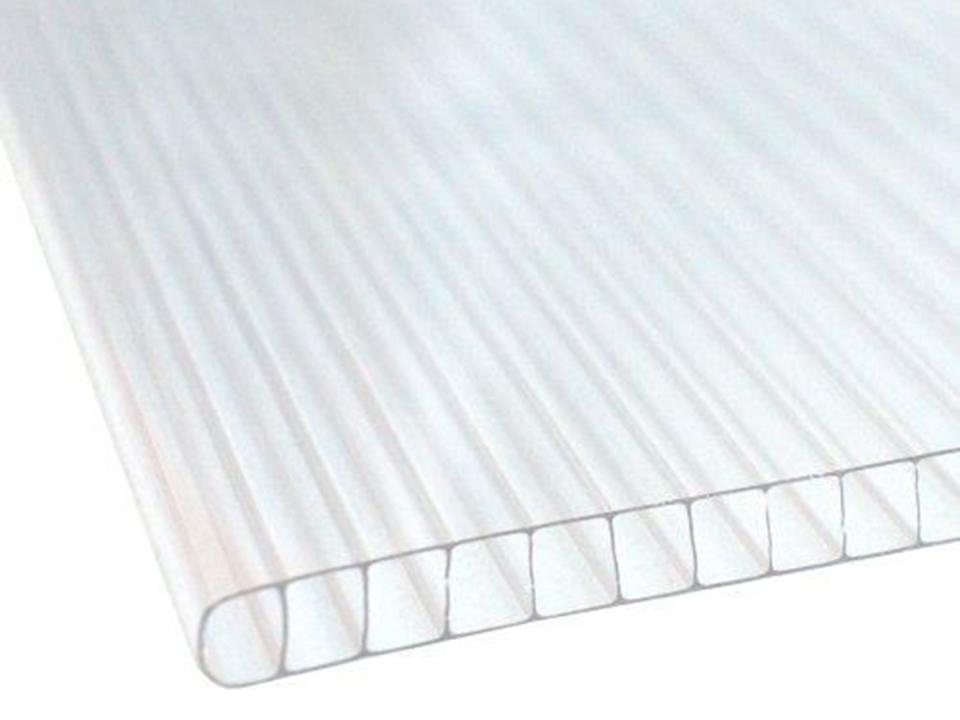
Assessing the performance of 4mm polycarbonate in a greenhouse setting involves examining its strengths, limitations, and overall suitability.
Thickness and Insulation:
While 4mm polycarbonate is suitable for many greenhouse applications, its insulation properties are not as high as thicker options. In colder climates, 4mm panels may require additional heating to maintain adequate temperatures during the winter.
Impact Resistance:
4mm polycarbonate is less impact-resistant compared to thicker options. In addition, consider the risk of damage from hail, falling branches, or accidental impacts when choosing this thickness.
Climate Considerations:
4mm polycarbonate may work well in milder climates with less extreme temperature fluctuations. In areas with harsh winters or scorching summers, thicker panels are often recommended to provide better insulation and protection.
Budget Considerations:
4mm polycarbonate is typically more budget-friendly than thicker alternatives. However, if budget constraints are a significant concern, 4mm panels can be a reasonable choice while still offering good light transmission and UV protection.
What Are The Other Polycarbonate Thickness Options ?
When it comes to selecting polycarbonate as a greenhouse covering, it’s essential to be aware of the various thickness options available.
6mm Polycarbonate:
Pros:
- Improved insulation compared to 4mm, making it suitable for regions with moderate climates.
- Better impact resistance than 4mm, offering some protection against hail and wind-blown debris.
- A balance between cost-effectiveness and performance for many greenhouse applications.
Cons:
- Less insulation compared to 8mm and 10mm, potentially requiring additional heating in colder climates.
- Not as impact-resistant as thicker options.
8mm Polycarbonate:
Pros:
- Enhanced insulation properties make it suitable for a wider range of climates, including regions with colder winters.
- Improved impact resistance compared to 4mm and 6mm, reducing the risk of damage.
- Offers better energy efficiency, potentially leading to long-term cost savings.
Cons:
- Higher upfront cost compared to 4mm or 6mm panels.
- May be overkill for greenhouse applications in milder climates.
10mm Polycarbonate:
Pros:
- Excellent insulation, making it ideal for harsh climates with extreme temperature variations.
- Superior impact resistance, protecting against hail, falling objects, and strong winds.
- Maximum energy efficiency, minimizing heating and cooling costs.
Cons:
- Highest upfront cost among the thickness options.
- Overwhelming for greenhouse applications in very mild climates.
How Can You Maintain and Take Proper Care ?
Maintaining and caring for your greenhouse is crucial to ensure its longevity and optimal functionality.
Cleaning:
- Use a mild soap or specialized greenhouse cleaning solution to clean polycarbonate panels. Gently rinse with a hose or soft sponge to avoid scratching.
- Regular cleaning ensures maximum light transmission.
UV Protection:
- Many polycarbonate panels come with UV-resistant coatings.
- Check the manufacturer’s guidelines and reapply UV protection as needed.
- Protect plants from excessive UV exposure, especially during peak sunlight hours.
Repairs:
Small scratches can often be removed with specialized polycarbonate scratch remover.
For larger damages, replace damaged panels promptly to maintain insulation and structural integrity. Moreover, ensure proper sealing to prevent leaks and drafts.
FAQ’s :
How thick should greenhouse polycarbonate be?
The appropriate thickness for greenhouse polycarbonate depends on factors like climate and budget. Common options include 4mm, 6mm, 8mm, and 10mm.
How strong is 4mm polycarbonate?
4mm polycarbonate is relatively strong but has limitations. It can withstand moderate impacts but may not be suitable for areas with harsh weather conditions or high impact risk.
What is the difference between 4mm and 6mm polycarbonate greenhouse?
The primary difference is thickness. 6mm polycarbonate offers better insulation and slightly higher impact resistance compared to 4mm, making it more suitable for colder climates.
What thickness should I use?
The choice of polycarbonate thickness depends on your specific needs. Consider factors like climate, greenhouse design, budget, and insulation requirements to make an informed decision.
Is 4 mil plastic thick enough for a greenhouse?
4 mil plastic is quite thin and may not provide sufficient insulation or durability for a greenhouse. Thicker options like polycarbonate or 6 mil plastic are often preferred.
What is the best thickness for greenhouse plastic?
The best thickness for greenhouse plastic depends on your location and climate. Common options are 6 mil and 8 mil plastic, providing a good balance between cost and performance. Thicker plastics offer better insulation but at a higher cost.
Final Words
In conclusion, after exploring the various facets of greenhouse covering materials and the considerations for selecting the appropriate polycarbonate thickness, I have gained a deeper understanding of the factors that contribute to a successful greenhouse setup.
When it comes to choosing between different materials like polycarbonate, glass, or polyethylene, it’s evident that polycarbonate offers a well-rounded combination of durability, insulation, light transmission, UV resistance, and impact resistance.
However, the decision regarding polycarbonate thickness should be guided by specific needs, considering climate, greenhouse design, budget constraints, desired lifespan, and energy efficiency goals. While 4mm polycarbonate can be suitable for certain applications, thicker options like 6mm, 8mm, or 10mm may offer better performance in challenging conditions.

